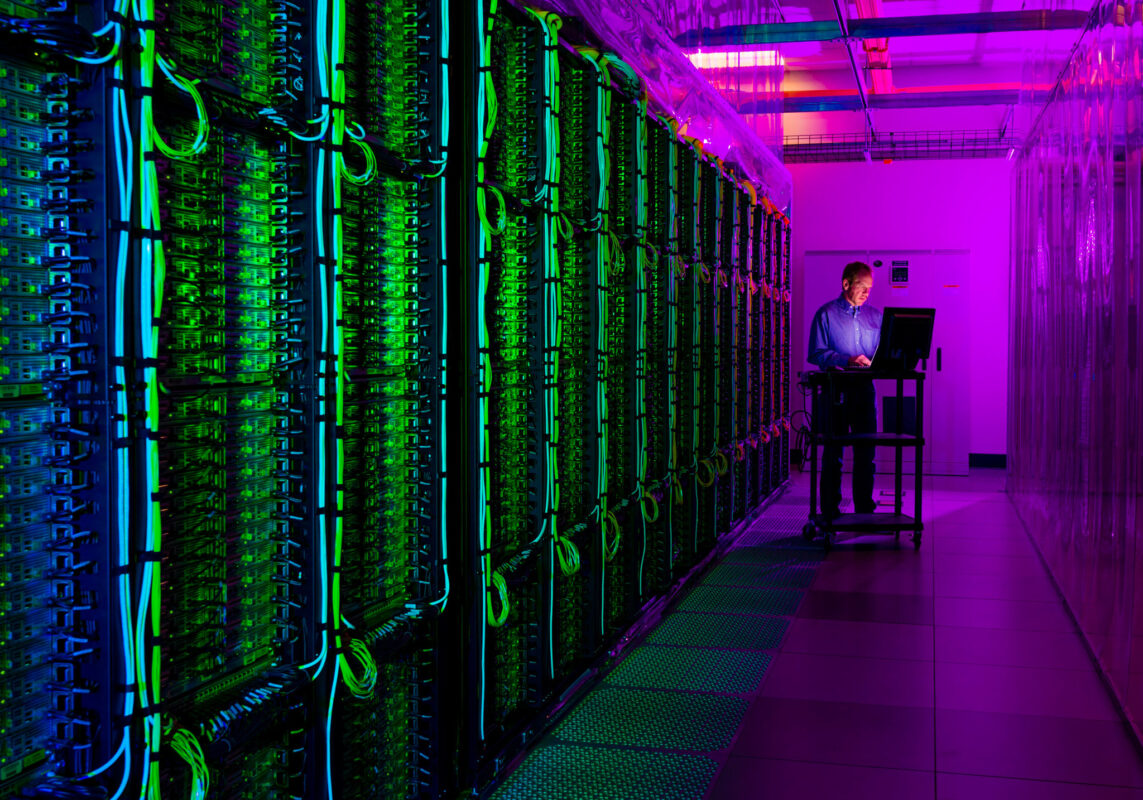
Unified Storage
Unified storage is a storage solution that combines different types of storage systems, such as file storage and block storage, into a single, integrated platform. The goal of unified storage is to simplify storage management, improve efficiency, and provide flexibility in meeting various storage needs within an organization.
Multiple Protocols: Unified storage systems typically support multiple storage protocols, including Network Attached Storage (NAS) for file-level access and Storage Area Network (SAN) for block-level access. This allows organizations to use a single storage platform for a wide range of applications and workloads.
Centralized Management: Unified storage systems provide a centralized management interface, making it easier for administrators to configure, monitor, and maintain storage resources. This simplifies storage management tasks compared to managing separate NAS and SAN systems.
Cost Savings: Consolidating storage into a unified platform can lead to cost savings in terms of hardware, software licensing, and administrative overhead. It reduces the need for separate storage silos, which can be costly to purchase and manage.
How unified storage works
Unified storage is a platform with storage capacity connected to a network that provides file-based and block-based data storage services to other devices on the network. Unified storage uses standard file protocols such as Common Internet File System (CIFS) and Network File System (NFS) and standard block protocols like Fibre Channel (FC) and Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) to allow users and applications to access data consolidated on a single device.
Benefits of unified storage
Large numbers and various types and release levels of direct-attached storage or internal storage can be difficult to manage and protect as well as costly due to very low total utilization rates. Unified storage provides the cost savings and simplicity of consolidating storage over an existing networks. With the option of tiered or all-flash storage, and the efficiency of data compression and deduplication, Unity delivers the flexibility required by virtual server environments.

Data Migration – Data Storage
Dell Technologies provides data migration services to help you move data and workloads seamlessly with flexibility and simplicity.
Data Storage
Dell Technologies provides a broad range of enterprise data storage solutions and products to solve the data storage challenges.

Hybrid Storage
Dell Technologies provides hybrid storage solutions to minimize the burden on IT teams and reduce the cost and complexity of data management.
Cloud Storage – Data Storage
Dell ECS is an object storage platform that empowers organizations to use Cloud storage for unstructured data.


