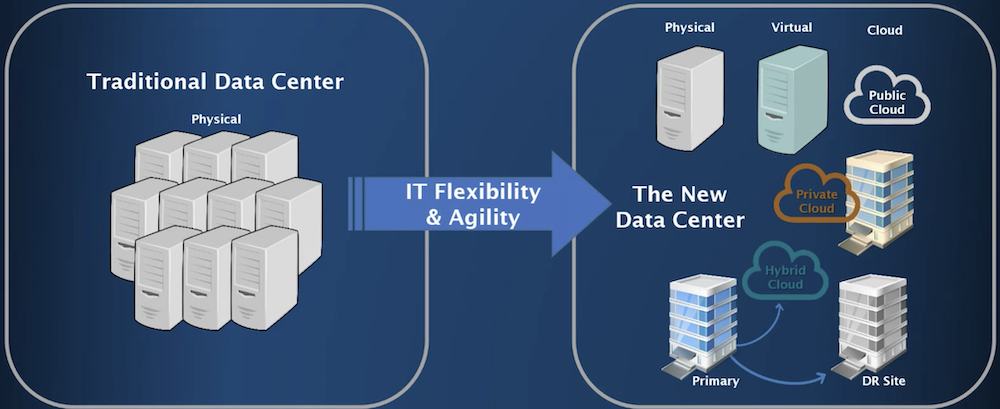
HA & DR SITES :-
High Availability (HA) and Disaster Recovery (DR) sites are critical components of a comprehensive IT strategy. These sites are designed to ensure that critical systems and data remain available and accessible in the event of an unexpected outage or disaster.
High Availability (HA) refers to the ability of a system or application to remain available and functional in the event of a hardware or software failure. HA systems are designed to minimize downtime and ensure that users can continue to access critical applications and data without interruption. HA systems are typically implemented through redundancy and failover mechanisms, such as redundant servers, storage, and network components. If one component fails, the system automatically switches to a backup component, ensuring that the system remains operational.
Disaster Recovery (DR) refers to the ability to recover data and systems in the event of a major outage or disaster, such as a natural disaster, cyber attack, or equipment failure. DR systems are designed to minimize downtime and data loss, and to ensure that critical systems and data can be restored quickly and efficiently. DR systems are typically implemented through offsite replication of data and systems to a secondary location. In the event of a disaster, systems can be restored from the offsite backup, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Both HA and DR systems are critical components of a comprehensive IT strategy, and they must be carefully designed, implemented, and tested to ensure that they are effective and reliable.
HIGH AVAILABILITY :-
High Availability (HA) refers to a system or application's ability to remain available and operational with minimal downtime or service interruption, even in the event of hardware or software failures.
To achieve high availability, a system or application must be designed with redundancy and failover mechanisms that allow it to continue functioning even if one or more components fail. These mechanisms may include:
1 - Redundant hardware components: For example, multiple servers, storage devices, or network switches may be used to ensure that there is no single point of failure.
2 - Automatic failover: If a component fails, the system must automatically switch to a redundant component to ensure that service is not interrupted.
3 - Load balancing: Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple servers to prevent any single server from becoming overloaded and failing.
4 - Monitoring and alerting: The system must be monitored to quickly identify any issues or failures, and alerts should be sent to IT staff so they can take action to address the issue.
5 - Regular maintenance: Regular maintenance, such as software updates and hardware upgrades, should be performed to prevent failures from occurring in the first place.
High availability is critical for mission-critical applications and systems, such as e-commerce websites, banking systems, and healthcare applications, where even brief periods of downtime can have significant consequences. By implementing a high availability architecture, organizations can ensure that their critical systems and applications remain available and operational, even in the face of unexpected failures.
DISASTER RECOVERY :-
Disaster Recovery (DR) refers to the process of recovering IT systems and data following a major outage or disaster, such as a natural disaster, cyber attack, or equipment failure. The goal of DR is to minimize downtime and data loss and to ensure that critical systems and data can be restored quickly and efficiently. To implement an effective DR plan, organizations typically follow a series of steps:
1 - Business impact analysis: This involves identifying critical systems and data and assessing the potential impact of a disaster on the organization's operations.
2 - Risk assessment: This involves identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities that could lead to a disaster and assessing their likelihood and impact.
3 - DR strategy development: Based on the business impact analysis and risk assessment, a DR strategy is developed that outlines the steps required to recover critical systems and data in the event of a disaster.
4 - DR plan implementation: The DR plan is implemented, including the installation of backup systems, data replication, and testing procedures.
5 - DR plan testing: The DR plan is tested to ensure that it is effective and can be executed quickly and efficiently in the event of a disaster.
6 - DR plan maintenance: The DR plan is regularly reviewed and updated to ensure that it remains effective and up-to-date.
By implementing a comprehensive DR plan, organizations can ensure that critical systems and data can be recovered quickly and efficiently in the event of a disaster, minimizing downtime and data loss and ensuring that business operations can be restored as quickly as possible.
